# electron-tabs
> Simple tabs for Electron applications
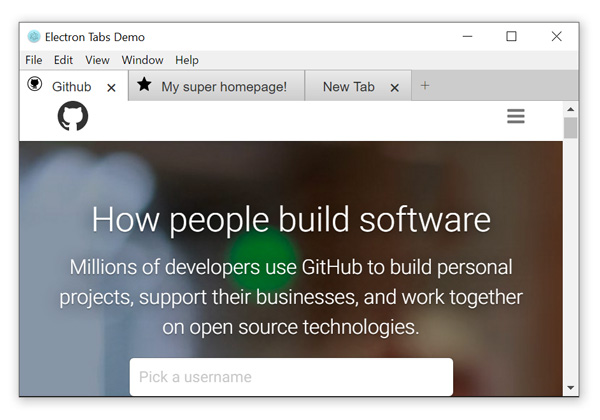
## Installation
```
$ npm install --save electron-tabs
```
## Usage
Add the following elements to the app page:
```html
```
And call the module in the renderer process:
```javascript
const TabGroup = require("electron-tabs");
```
Then you can initialize a tab group and add tabs to it:
```javascript
let tabGroup = new TabGroup();
let tab = tabGroup.addTab({
title: "Electron",
src: "http://electron.atom.io",
visible: true
});
```
If you don't want to write your own styles, you can also insert the sample electron-tabs stylesheet in the page header:
```html
```
## API
### Tab Group
Represents the main tab container.
#### `new TabGroup(options)`
`options` must be an object. The following options are available:
* `tabContainerSelector` (default: `".etabs-tabs"`): CSS selector to target the element where tabs are inserted.
* `buttonsContainerSelector` (default: `".etabs-buttons"`): CSS selector to target the element where the "New Tab" button are inserted.
* `viewContainerSelector` (default: `".etabs-views"`): CSS selector to target the element where the view are inserted.
* `tabClass` (default: `"etabs-tab"`): class to add to tab elements.
* `viewClass` (default: `"etabs-view"`): class to add to webview elements.
* `closeButtonText` (default: `"✖"`): "close tab" button text.
* `newTabButtonText` (default: `"+"`): "New Tab" button text.
* `newTab` (default: `undefined`): arguments to use when `.addTab()` is called without parameters. It can be an object or a function which returns an object. It determines the options to use when the "New Tab" button is triggered. If you leave it undefined then the "New Tab" button won't be displayed.
* `ready` (default: `undefined`): a callback function to call once the tab group is ready. The `TabGroup` instance is passed as the only parameter.
#### `tabGroup.addTab(options)`
Add a new tab to the tab group and returns a `Tab` instance.
* `title`: tab title.
* `src`: URL to the page which will be loaded into the view. This is actually the same than `options.webview.src`.
* `iconURL`: optional URL to the tab icon.
* `closable` (default: `true`): if set to `true` the close button won't be displayed and the user won't be able to close the tab. See also `tab.close()`.
* `webviewAttributes`: attributes to add to the webview tag. See [webview documentation](http://electron.atom.io/docs/api/web-view-tag/#tag-attributes).
* `visible` (default: `true`): set this to `false` if you don't want to display the tab once it is loaded. If set to `false` then you will need to call `tab.show()` to display the tab.
* `active` (default: `false`): set this to `true` if you want to activate the tab once it is loaded. Otherwise you will need to call `tab.activate()`.
* `ready`: a callback function to call once the tab is ready. The `Tab` instance is passed as the only parameter.
#### `tabGroup.getTab(id)`
Retrieve an instance of `Tab` from its `id` (return `null` if not found).
#### `tabGroup.getActiveTab()`
Return the currently active tab (otherwise return `null`).
### Tab
Instances of `Tab` are returned by the `tabGroup.addTab()` method.
#### `tab.setTitle(title)`
Set tab title.
#### `tab.getTitle()`
Get current tab title.
#### `tab.setIcon(iconURL)`
Set tab icon (an URL must be given).
#### `tab.getIcon()`
Get current tab icon URL.
#### `tab.activate()`
Activate this tab. The class "active" is added to the active tab.
#### `tab.show(flag)`
Toggle the "visible" class on the tab. `tab.hide()` is an alias to `tab.show(false)`.
#### `tab.flash(flag)`
Toggle the "flash" class on the tab. `tab.unflash()` is an alias to `tab.flash(false)`.
#### `tab.close(force)`
Close the tab (and activate another tab if relevant). When `force` is set to `true` the tab will be closed even if it is not `closable`.
### Access webview element
You can access the webview element and use its methods with through the `Tab.webview` attribute. See [webview documentation](http://electron.atom.io/docs/api/web-view-tag/#methods).
```javascript
let webview = tab.webview;
webview.loadURL("file://path/to/new/page.html");
```
### Events
The following events are available:
* `tabGroup.on("tab-added", (tab, tabGroup) => { ... });`
* `tabGroup.on("tab-removed", (tab, tabGroup) => { ... });`
* `tabGroup.on("tab-active", (tab, tabGroup) => { ... });`
* `tab.on("title-changed", (title, tab) => { ... });`
* `tab.on("icon-changed", (iconURL, tab) => { ... });`
* `tab.on("active", (tab) => { ... });`
* `tab.on("visible", (tab) => { ... });`
* `tab.on("hidden", (tab) => { ... });`
* `tab.on("flash", (tab) => { ... });`
* `tab.on("unflash", (tab) => { ... });`
* `tab.on("close", (tab) => { ... });`
## Drag and drop support
Electron-tabs is compatible with [Dragula](https://github.com/bevacqua/dragula) so you can easily make your tabs draggable.
Install Dragula:
```
npm install dragula --save
```
Don't forget to add a link to its stylesheet in the header:
```html
```
Then call Dragula in your script once tabGroup is ready:
```javascript
const TabGroup = require("electron-tabs");
const dragula = require("dragula");
var tabGroup = new TabGroup({
ready: function (tabGroup) {
dragula([tabGroup.tabContainer], {
direction: "horizontal"
});
}
});
```
## License
The MIT License (MIT) - Copyright (c) 2016 Thomas Brouard